前言
一般来说离散的课设都是给一大堆题目然后自己选的
我选的是合式公式的真值表和成真成假赋值
算是里面相对难的
(别的是真挺简单的)
课设我是拿C#写的(人生苦短,还是用好用的语言吧)
应该常用的.net版本都能跑起来吧,代码里没怎么用新特性
(我用的是.net 6.0)C#的语法还是挺好懂得,用过C系语言看懂应该问题不大
同样,可以在本文最后复制所有的原码
(就一个文件,就不发本站的gitea了)
(报告自己写写挺快的)
<0x00> 如何解析合式公式
在尝试解析合式公式前,我们可以先想想我们该如何解析一般加减乘除的
(所谓解析就是判断计算的优先级)
比方说我们有公式1+2*3/(4-5)
按运算优先级加上括号就是(1+((2*3)/(4-5)))
所以说我们该如何让计算机按这样的优先级计算呢
双栈法
准备两个栈,一个是运算数栈,一个是运算符栈
运算式在运算前先在首位各加括号(确保最后会栈空)
然后从左向右遍历运算式
遇到(时直接压入运算符栈,遇到数字压入运算数栈
当遇到运算符时,先检查当前运算符优先级是否大于栈顶运算符,如是,直接压入
如果不是,那么就先进行弹出操作
每次弹出都是弹出一个运算符与两个运算数,并将运算结果再压入运算符栈中
重复弹出,直到当前运算符优先级大于运算符栈顶的运算符优先级为止
如果遍历过程中遇到),则反复进行弹出操作,直到弹出一个(为止
同样的思路也可以运用在合式公式上
具体流程如下:
- 1 给公式的左右套上括号
- 2 从左向右读取
- 3 如果遇到
(,将(压入运算符栈后继续 - 4 如果遇到运算数,压入
操作数栈后继续 - 5 如果遇到运算符,按照以下规则:
- a 如果
运算符栈为空或栈顶元素优先级小于当前运算符,直接压入运算符栈 - b 若遇到栈顶元素为
┐(非),需要弹出所有的连续┐(非),弹出此运算符再弹出一个运算数,并将运算结果压回操作数栈 - c 其余情况按照弹出一个运算符并弹出两个操作数的规则,反复弹出,并将结合结果压回操作数栈,直到能按照
5.a压入运算符栈
- a 如果
- 6 遇到
)时,反复按照规则弹出,直到运算符栈顶为(,最后移除栈顶的( - 7 读取完毕后,
操作数栈留下的东西就是公式答案
这个就不再用动画演示了,本质上就是一般+-*/运算双栈法的变种
唯一不一样的就是对于┐(非)要注意连续弹出问题
因为┐(非)是一个右结合单目运算符,而且优先级最高
如果不先处理调连续的┐(非)容易解析出问题
所以要把连续的┐(非)全弹出,当作一个整体,这样才能出正确答案
<0x01> 由双栈法构建运算树
目前我们已经有方法解析合式公式了,但有一个问题
我们的题目要求给出一个真值表
如果每次计算我们都要先解析一遍合式公式的话,效率不会很高
所以我们要用一种数据结构来保存计算的结构
每个单一操作数数可以改变对应的真假指派(就是T/F)
对于一个计算的过程,我们可以抽象成一个树
所有的操作数都是树的叶子(最末端的节点)
操作数由运算符连接,合成一个新节点
如此嵌套,最后连接在一个根节点上
每次计算时,先给操作数真假指派,然后走遍计算树,根节点的值就是公式的计算结果
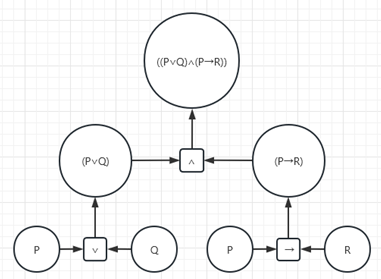
就是这么个结构
怎么构建这棵树呢,其实之前的双栈法里就有这个答案
我们仅需略微更改下代码,操作数栈不存储运算结果而是存储运算节点
这样走一遍公式就相当于构建了一颗计算树
最后只要存储根节点就好了
<0x02> 逻辑实现
按从低到高的优先级列出运算符的枚举类型
public enum Operator//枚举运算符
{
LeftBracket,//左括号
XNOR,//双条件运算符
Odds,//条件运算符
Or,//析取运算符
And,//合取运算符
Not,//取反运算符
}
定义计算树的计算节点类(仅列出定义)
internal class CalculateNode//定义计算节点
{
CalculateNode? left;//运算符左边
CalculateNode? right;//运算符右边
Operator oper;//节点的运算符
bool ans;//该节点答案
internal CalculateNode(bool ans);//末节点构造方法
internal CalculateNode(CalculateNode? left, CalculateNode right, Operatoroper);//计算节点构造方法
static bool Odds(bool a, bool b);//单独定义条件运算符
bool Calculate(CalculateNode node);//从某节点递归计算
internal bool Calculate();//提供一个入口
internal void ChangeAns(bool ans);//改变末节点的值
}
可以看到,每个计算节点包含运算符,左边节点,右边节点,节点答案
操作数节点仅有节点答案(所以左右节点的类型是可空类型)
因为条件运算符没有现成的运算符,所以自己写一个Calculate(CalculateNode node)通过递归来遍历每个节点并给出每个节点的答案Calculate()专门给外部调用的,里面就一句return Calculate(this);ChangeAns(bool ans)用来改变操作数的真假指派
定义WellFormedFormula类(仅列出定义)
public class WellFormedFormula
{
string formula;//原公式
Dictionary<string, CalculateNode> map;//以string方式索引所有节点
Dictionary<int, string> dic;//以int方式索引所有根节点的名字
CalculateNode root;//最终答案节点
bool[] truthTable;//真值表
private static bool IsOperator(char c);//判断是否为二元运算符
private static char OperatorToChar(Operator op);//运算符换成char
private static Operator CharToOperator(char c);//char换成运算符
private bool Verify();//验证公式是否有效
private void Init();//初始化计算树
public WellFormedFormula(string formula);//构造方法
public bool Calculate(int n);
public bool Calculate(Dictionary<string, bool> keyValuePairs);//单独计算用
private void CalculateAll();//全计算
public void ChangeFormula(string formula);//更改公式
public void ShowrTruthTable();//展示真值表
public void ShowFormula();//展示公式
public void ShowAllNode();//展示所有节点信息,用于调试
public void ShowTrueAssignment();//展示所有成真赋值
public void ShowFalseAssignment();//展示所有成假赋值
public void ShowDNF();//主析取范式
public void ShowCNF();//主合取范式
}
最关键的是Init()方法,别的实现不难
private void Init()//初始化计算树(略去实现细节)
{
Verify();//验证
//获取所有的变量
//...
//构建计算树
//...
CalculateAll();//顺便把真值表给算了
}
在Init()中,先验证公式合法性(防输入错误)
然后会先遍历遍公式,获取所有的变量名并创建操作数节点(末节点)
然后再遍历一遍,构建计算树
构建完成后,root指向根节点,map可以按节点名索引到对应的操作数节点dic可以按index索引到节点名字(方便遍历)
构建完再计算所有的赋值情况,直接得出真值表
其他的方法都是调用真值表答案,不会再计算公式
构建过程就是双栈法构建
附录,所有的代码
//核心逻辑实现
namespace CStest
{
public enum Operator//枚举运算符
{
LeftBracket,//左括号
XNOR,//双条件运算符
Odds,//条件运算符
Or,//析取运算符
And,//合取运算符
Not,//取反运算符
}
internal class CalculateNode//定义计算节点
{
CalculateNode? left;//运算符左边
CalculateNode? right;//运算符右边
Operator oper;//节点的运算符
bool ans;//该节点答案
internal CalculateNode(bool ans)//末节点构造方法
{
left = null;
right = null;
this.ans = ans;
}
internal CalculateNode(CalculateNode? left, CalculateNode right, Operator oper)//计算节点构造方法
{
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.oper = oper;
}
static bool Odds(bool a, bool b)//单独定义条件运算符
{
if (!a)
{
return true;
}
else
{
if (b)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
bool Calculate(CalculateNode node)//从某节点递归计算
{
if (node.right == null)//递归边界条件
{
return node.ans;
}
switch (node.oper)
{
case Operator.Not:
node.ans = !Calculate(node.right);
break;
case Operator.And:
node.ans = Calculate(node.left) && Calculate(node.right);
break;
case Operator.Or:
node.ans = Calculate(node.left) || Calculate(node.right);
break;
case Operator.Odds:
node.ans = Odds(Calculate(node.left), Calculate(node.right));
break;
case Operator.XNOR:
node.ans = !(Calculate(node.left) ^ Calculate(node.right));
break;
}
return node.ans;
}
internal bool Calculate()//提供一个入口
{
return Calculate(this);
}
internal void ChangeAns(bool ans)//改变末节点的值
{
this.ans = ans;
}
}
public class WellFormedFormula
{
string formula;//原公式
Dictionary<string, CalculateNode> map;//以string方式索引所有节点
Dictionary<int, string> dic;//以int方式索引所有根节点的名字
CalculateNode root;//最终答案节点
bool[] truthTable;//真值表
private static bool IsOperator(char c)//判断是否为二元运算符
{
return c == '∧' || c == '∨' || c == '→' || c == '⊙';
}
private static char OperatorToChar(Operator op)//运算符换成char
{
switch (op)
{
case Operator.And: return '∧';
case Operator.Or: return '∨';
case Operator.Odds: return '→';
case Operator.XNOR: return '⊙';
}
return ' ';
}
private static Operator CharToOperator(char c)//char换成运算符
{
switch (c)
{
case '∧': return Operator.And;
case '∨': return Operator.Or;
case '→': return Operator.Odds;
case '⊙': return Operator.XNOR;
}
return Operator.LeftBracket;
}
private bool Verify()//验证公式是否有效
{
if (IsOperator(formula[0]) || formula[^1] == '┐' || IsOperator(formula[^1]))
{
throw new Exception("Error in formula");//在首尾出现了不该出现的运算符
}
int l = 0;//统计左括号
int r = 0;//统计右括号
for (int i = 0; i < formula.Length; i++)
{
if (formula[i] == '(')
{
l++;
}
else if (formula[i] == ')')
{
r++;
}
if (formula[i] == '┐')
{
if (IsOperator(formula[i + 1]))
{
throw new Exception("Error in formula");//取反运算符后接别的运算符
}
}
if (IsOperator(formula[i]))
{
if (IsOperator(formula[i - 1]))
{
throw new Exception("Error in formula");
}
if (IsOperator(formula[i + 1]) || formula[i + 1] == '┐')
{
throw new Exception("Error in formula");
}
}//都是判断多个运算符不应该相连的情况
}
if (l != r)
{
throw new Exception("Error in formula");//左右括号数不匹配
}
return true;
}
private void Init()//初始化计算树
{
Verify();//验证
string formula = "(" + this.formula + ")";
//获取所有的变量
int index = 0;
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < formula.Length; i++)
{
if (flag && formula[i] != '(' && formula[i] != '┐' && !IsOperator(formula[i]))
{
index = i;
flag = false;
}
else if (formula[i] == ')' || formula[i] == '┐' || IsOperator(formula[i]))
{
if (index != i && !flag && !map.ContainsKey(formula[index..i]))
{
map.Add(formula[index..i], new CalculateNode(false));
dic.Add(dic.Count, formula[index..i]);
}
flag = true;
}
}
flag = true;
//构建计算树
Stack<string> v = new Stack<string>();//操作数栈
Stack<Operator> op = new Stack<Operator>();//运算符栈
string sa;
string sb;//两个临时string变量
for (int i = 0; i < formula.Length; i++)
{
if (formula[i] == '(')//左括号直接压入栈
{
op.Push(Operator.LeftBracket);
continue;
}
if (flag && formula[i] != ')' && formula[i] != '┐' && !IsOperator(formula[i]))
{
index = i;
flag = false;
}
else if (formula[i] == ')' || formula[i] == '┐' || IsOperator(formula[i]))
{
if (index != i && !flag)//压入操作数
{
v.Push(formula[index..i]);
flag = true;
}
if (formula[i] == '┐')
{
op.Push(Operator.Not);//取反直接压入
}
else if (formula[i] == ')')//遇到右括号不断弹出,直到遇到左括号
{
while (op.Peek() != Operator.LeftBracket)
{
if (op.Peek() == Operator.Not)
{
sa = v.Pop();
map.Add("(┐" + sa + ")", new CalculateNode(null, map[sa], Operator.Not));
v.Push("(┐" + sa + ")");
break;
}
else
{
sa = v.Pop();
sb = v.Pop();
map.Add("(" + sb + OperatorToChar(op.Peek()) + sa + ")", new CalculateNode(map[sb], map[sa], op.Peek()));
v.Push("(" + sb + OperatorToChar(op.Peek()) + sa + ")");
}
op.Pop();
}
op.Pop();//弹出左括号
}
else
{
if (op.Count != 0 && CharToOperator(formula[i]) < op.Peek())
{
if (op.Peek() == Operator.Not)
{
do//由于取反运算可多个连接,所以要一次性弹出所有连续的取反运算
{
op.Pop();
sa = v.Pop();
map.Add("(┐" + sa + ")", new CalculateNode(null, map[sa], Operator.Not));
v.Push("(┐" + sa + ")");
} while (op.Peek() == Operator.Not);
}
else
{
sa = v.Pop();
sb = v.Pop();
map.Add("(" + sb + OperatorToChar(op.Peek()) + sa + ")", new CalculateNode(map[sb], map[sa], op.Peek()));
v.Push("(" + sb + OperatorToChar(op.Peek()) + sa + ")");
op.Pop();
}
}
op.Push(CharToOperator(formula[i]));//最后把当前运算符压入
}
}
}
root = map[v.Pop()];//最后的操作数就是root节点
truthTable = new bool[(int)Math.Pow(2, dic.Count)];
CalculateAll();//顺便把真值表给算了
}
public WellFormedFormula(string formula)//构造方法
{
map = new Dictionary<string, CalculateNode>();
dic = new Dictionary<int, string>();
this.formula = formula;
Init();
}
public bool Calculate(int n)
{
return truthTable[n];
}
public bool Calculate(Dictionary<string, bool> keyValuePairs)//单独计算用
{
if (keyValuePairs.Count != dic.Count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
foreach (var kv in keyValuePairs)
{
map[kv.Key].ChangeAns(kv.Value);
}
return root.Calculate();
}
private void CalculateAll()//全计算
{
Stack<bool> b = new Stack<bool>();
int index;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)Math.Pow(2, dic.Count); i++)
{
b.Clear();
index = i;
while (index > 0)
{
if (index % 2 == 1)
{
b.Push(true);
}
else
{
b.Push(false);
}
index /= 2;
}
while (b.Count < dic.Count)
{
b.Push(false);
}
for (int j = 0; j < dic.Count; j++)
{
map[dic[j]].ChangeAns(b.Pop());
}
truthTable[i] = root.Calculate();
}
}
public void ChangeFormula(string formula)//更改公式
{
this.formula = formula;
map.Clear();
dic.Clear();
Init();
}
public void ShowrTruthTable()//展示真值表
{
for (int i = 0; i < dic.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write(dic[i] + '\t');
}
Console.WriteLine(formula);
Stack<bool> b = new Stack<bool>();
int index;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)Math.Pow(2, dic.Count); i++)
{
index = i;
while (index > 0)
{
if (index % 2 == 1)
{
b.Push(true);
}
else
{
b.Push(false);
}
index /= 2;
}
while (b.Count < dic.Count)
{
b.Push(false);
}
while (b.Count > 0)
{
if (b.Pop())
{
Console.Write("T\t");
}
else
{
Console.Write("F\t");
}
}
if (truthTable[i])
{
Console.WriteLine("T");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("F");
}
}
}
public void ShowFormula()//展示公式
{
Console.WriteLine(formula);
}
public void ShowAllNode()//展示所有节点信息,用于调试
{
Console.Write("| ");
foreach (var m in map)
{
Console.Write(m.Key + " | ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
public void ShowTrueAssignment()//展示所有成真赋值
{
Console.Write("All true assignment: ");
for (int i = 0; i < dic.Count; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
{
Console.Write(dic[i]);
}
else
{
Console.Write(" | " + dic[i]);
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
int index;
Stack<byte> temp = new Stack<byte>();
for (int i = 0; i < (int)Math.Pow(2, dic.Count); i++)
{
temp.Clear();
if (truthTable[i])
{
index = i;
while (index > 0)
{
temp.Push((byte)(index % 2));
index /= 2;
}
while (temp.Count < dic.Count)
{
temp.Push(0);
}
while (temp.Count > 0)
{
Console.Write(temp.Pop());
}
Console.WriteLine("(" + i + ")");
}
}
}
public void ShowFalseAssignment()//展示所有成假赋值
{
Console.Write("All false assignment: ");
for (int i = 0; i < dic.Count; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
{
Console.Write(dic[i]);
}
else
{
Console.Write(" | " + dic[i]);
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
int index;
Stack<byte> temp = new Stack<byte>();
for (int i = 0; i < (int)Math.Pow(2, dic.Count); i++)
{
temp.Clear();
if (!truthTable[i])
{
index = i;
while (index > 0)
{
temp.Push((byte)(index % 2));
index /= 2;
}
while (temp.Count < dic.Count)
{
temp.Push(0);
}
while (temp.Count > 0)
{
Console.Write(temp.Pop());
}
Console.WriteLine("(" + i + ")");
}
}
}
public void ShowDNF()//主析取范式
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)Math.Pow(2, dic.Count); i++)
{
if (truthTable[i])
{
if (count == 0)
{
Console.Write("m(" + i + ")");
}
else
{
Console.Write("∨m(" + i + ")");
}
count++;
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
public void ShowCNF()//主合取范式
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)Math.Pow(2, dic.Count); i++)
{
if (!truthTable[i])
{
if (count == 0)
{
Console.Write("M(" + i + ")");
}
else
{
Console.Write("∧M(" + i + ")");
}
count++;
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
//main.cs
namespace CTest{
public class test
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
WellFormedFormula w = new WellFormedFormula("(P∨Q)∧(P→R)");
w.ShowAllNode();
w.ShowrTruthTable();
w.ShowTrueAssignment();
w.ShowFalseAssignment();
w.ShowCNF();
w.ShowDNF();
}
}
}